The digestive system is the group of organs and tissues that work together to break down food that can be absorbed by the body.
The teeth help to break down food into smaller pieces by cutting, grinding, and mixing food as you chew.
The digestion is the process by which the body breaks down food into nutrients that can be used for energy.
Digestive system worksheet

Click on each link to download our specially designed Digestive system worksheets for class 4 containing various question types.
We are now on WhatsApp – Click to Join Us
Read Also:
Free Science worksheets for Class 4
NCERT Hindi Worksheets for Class 4
What is Digestive system?
The digestive system plays an important role in providing the body with energy and nutrients needed for growth and maintenance.

The digestive system includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
Digestion starts in the mouth, where food is chewed and mixed with saliva, and ends in the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream.
Functions of teeth
The primary function of teeth is to help you swallow food by cutting, grinding, and mixing as you chew.
Moreover, teeth also help you breathe and talk, as well it is the foundation for shaping the lower portion of your face.
Teeth are one of the strongest parts of human body. They’re made from proteins such as collagen, and minerals such as calcium.
A child have 20 primary teeth known as temporary teeth or milk teeth. When a child is around six years, the milk teeth begin to fall and a new set of teeth grows. An adult have 32 primary teeth, known as permanent teeth. There are 16 teeth in the upper jaw and 16 teeth in the lower jaw.
Types of teeth
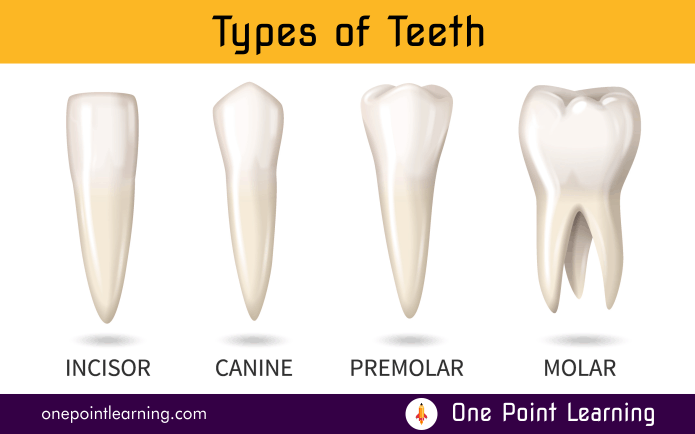
Teeth have different shapes and functions depending on their location in the mouth. There are four main categories of human teeth. They are Incisors, Canines, Premolars and Molars.
- Incisors: Incisors are shaped like small chisels and are located in the front part of your mouth. These front teeth are used for biting and cutting.
- Canine: These teeth are sharp and pointed, used to tear and rip apart food. Canines are firmly rooted and usually have the longest root of all the teeth.
- Premolar: Premolars, are oval-shaped teeth. They have a flat surface with ridges for crushing and grinding food into smaller pieces
- Molars: These are the biggest and strongest teeth. Molars are used for grinding and chewing food. Molars are the teeth you use most for chewing.
Anatomy of Tooth
The tooth is made of two parts – the crown and the root.
The crown of a tooth is the top part that is exposed and visible above the gum.
The root of a tooth is inside the gum, holding the tooth in the mouth. Different types of teeth have a different number of roots and root formations.
The neck is the region of the tooth, where the crown meets the root.
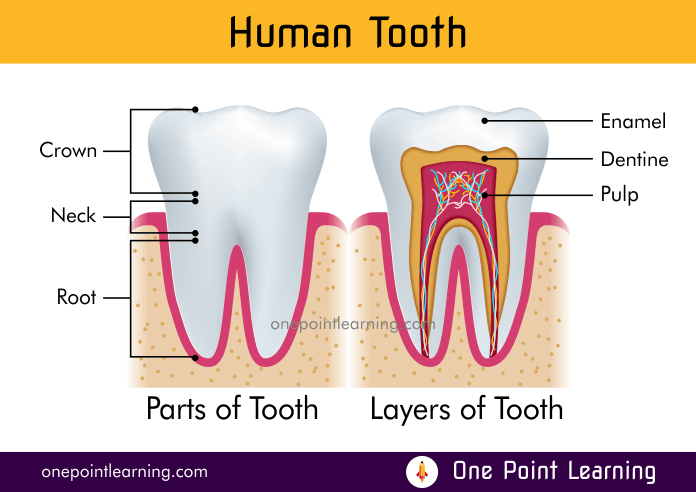
There are three main layers of tooth, Enamel, Dentine and pulp.
- Enamel: The hardest, white outer part of the tooth. Enamel is mostly made of calcium phosphate. It protects the tooth from wear and tear.
- Dentine: It is a layer under the enamel to support it. When the enamel is damaged, it causes sensitivity or pain.
- Pulp: The softer, living inner structure of teeth. Blood vessels and nerves run through the pulp of the teeth. It sends signals to the brain in case of toothache.
We are now on WhatsApp – Click to Join Us
Digestion process
Digestion is the process by which our body breaks down the food we eat into smaller pieces that can be absorbed by the body.
The digestion begins in the mouth, where food is chewed and mixed with saliva. Saliva contains enzymes that help break down the food and make it easier to swallow.
From the mouth, food travels down the esophagus and into the stomach. In the stomach, the food is mixed with stomach acid and enzymes that break down the proteins and fats in the food. The stomach also grinds the food into a liquid substance called chyme.
Next, the chyme moves into the small intestine, where it is mixed with enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver. These enzymes and bile help break down the remaining proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in the food.
Finally, the nutrients from the food are absorbed into the bloodstream and carried to the rest of the body to be used as energy.


