Adaptations in plants are a special features that have developed in plants over time to help them survive and reproduce in their specific environments.
Plants are amazing living organisms that have adapted to survive in almost every corner of our planet.
Moreover, plant adaptations can take various forms, including structural, behavioural, reproductive, and environmental adaptations. Plants have developed a range of adaptations that help them survive in different environments. These adaptations include leaves, roots, seeds, and flowers, as well as other characteristics such as thorns and spines.
The adaptations in plants ensure that they continue to thrive in various parts of the world and remain an essential part of our ecosystem.
Download free worksheets of Plant adaptations for Class 4, that contains various question types to help your kids better understand the topic and achieve good score.
Adaptations in Plants Worksheet

Read Also:
Free Science worksheets for Class 4
NCERT Hindi Worksheets for Class 4
What is an adaptation in plants?
Adaptations mean the special ability developed over a long time to help them live and grow well in their natural surroundings.
These adaptations can be in leaves, roots, seeds, and flowers, as well as other characteristics such as thorns and spines.
Importance of adaptations
Adaptations are very important in plants, as they help them to survive and reproduce in their natural habitat. Plants need adaptations to survive in different climates, having different amounts of sunlight, water, and nutrients.
Types of Adaptations
Plants have evolved a variety of adaptations over the time to help them survive in varied environments. These adaptations can be of three types:
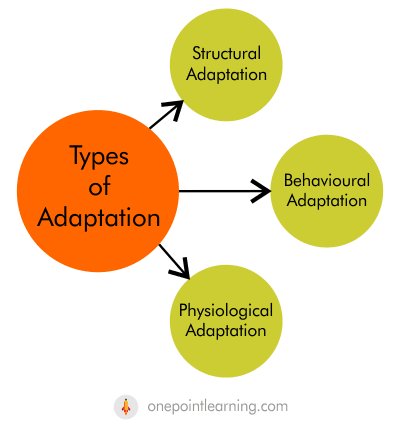
Structural adaptations: These are physical changes to a plant’s body that help it survive in its environment. For example, cacti have thick, waxy stems to store water and spines to protect themselves from predators.
Behavioural adaptations: These are changes in the way a plant behaves that help it survive in its environment. For example, some plants turn their leaves towards the sun to get more sunlight.
Physiological adaptations: These are changes in the way a plant’s body functions that help it survive in its environment. For example, some plants can close their stomata (small openings on the leaves) to reduce water loss.
Adaptations are important because they help plants to survive and reproduce in their environments. If a plant does not have the right adaptations, it may not be able to survive in its environment and may eventually die out.
Some examples of plant adaptations in different environments:
Desert: Cacti have thick, waxy stems and spines to store water and protect themselves from predators.
Rainforest: Lianas have long, flexible stems that allow them to climb tall trees and reach sunlight.
Arctic: Tundra plants have low-growing habits and dense root systems to protect them from the cold and wind.
Water: Lotus plants have water-repellent leaves that help them stay clean and dry.
Structural adaptations in plants
These adaptations in plants refer to physical changes in response to specific environmental conditions. These type of adaptations can be in roots, stems, leaves and flowers.
Roots:
Taproots: Some plants have a single, thick taproot that extends deep into the soil to access water reserves. This adaptation is common in desert plants like cacti.
Fibrous Roots: Other plants have a network of fine, fibrous roots near the surface, which are well-suited for absorbing moisture from shallow soils.
Stems:
Thorns and Spines: Some plants have evolved thorns and spines as a structural defence mechanism. Cacti are a well-known example.
Rhizomes: Rhizomes are underground stems that allow plants like bamboo to spread horizontally and reproduce.
Storage Tissues: Some plants have modified stems that store water or nutrients, such as aloe vera or agave.

Leaves:
Needle-like Leaves: Needle-like leaves, found in conifers like pine trees, reduce water loss due to their reduced surface area and a waxy surface.
Succulent Leaves: Succulent plants like aloe and cacti have thick, fleshy leaves that store water, helping them survive in desert environments.
Floating Leaves: Aquatic plants often have leaves that float on the water’s surface to capture sunlight for photosynthesis.
Flowers:
Showy Flowers: Some plants have brightly coloured and fragrant flowers to attract pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds. This adaptation increases the chances of successful pollination and reproduction.
Inconspicuous Flowers: Other plants, particularly wind-pollinated species like grasses, have inconspicuous and simple flowers, as they do not rely on attracting pollinators.
Adaptations based on Habitat
The natural home of a plant or an animal where they live and reproduce is called its habitat. Different habitats present different challenges and opportunities. Plants can be divided into two major groups based on their habitat.
Terrestrial Plants: The plants that grow on land
Aquatic plants: the plants that grow in water
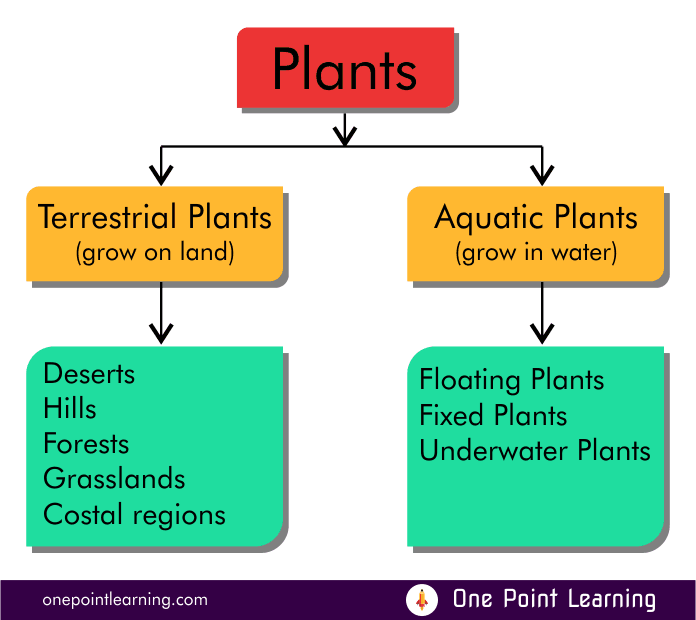
Terrestrial Plants
They are found in habitats such as deserts, plains, forests, hills, marshes costal and grasslands regions.
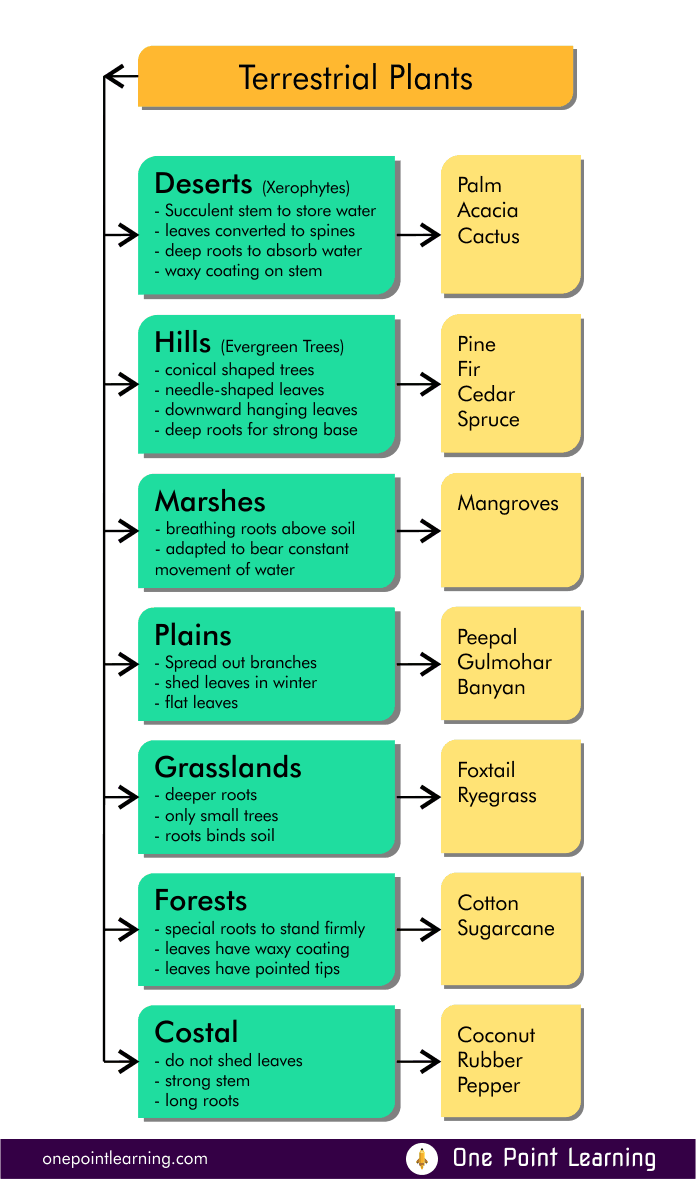
These are some examples of how plants have adapted to different habitats. These adaptations help plants survive and compete in their specific environments, helping them to preserve their species.



