Get ready to explore the incredible diversity of life on Earth! In this Class 6 Science chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of plants and animals.
We’ll learn how to classify them based on their similarities and differences, and discover the amazing adaptations that help them survive in various environments.
Here’s a glimpse of what you’ll learn:
- What is biodiversity?
- How to classify plants and animals
- The different types of plants (herbs, shrubs, trees, dicots, monocots)
- Animal adaptations for survival
- The importance of protecting biodiversity
Let’s start the exciting journey to uncover the wonders of nature!
Class 6 Science chapter 2 Worksheet

Download our diversity in the living world worksheet today and unlock a door to success.
Click to Join Us on WhatsApp Channel for latest updates!
Also download:
Class 6 Hindi Worksheet with Answers
Science Worksheets for Class 6
Ganita Prakash Class 6 Solutions
Diversity in the living world Notes
Introduction
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth. This includes all living things, from the smallest bacteria to the largest whales.
Why is biodiversity important?
It helps maintain the ecological balance of our planet and provides us with essential resources like food, medicine, and clean air.
Grouping of Plants
Based on similarities and differences: We can group plants based on their features like roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and seeds.
Grouping: Arranging things into groups based on common features is called grouping.
Classification of plants:
- Herbs: These are small plants with soft stems. Examples include grass, wheat, and spinach.
- Shrubs: These are medium-sized plants with woody stems. Examples include roses, jasmine, and hibiscus.
- Trees: These are tall plants with woody trunks. Examples include oak, mango, and coconut.
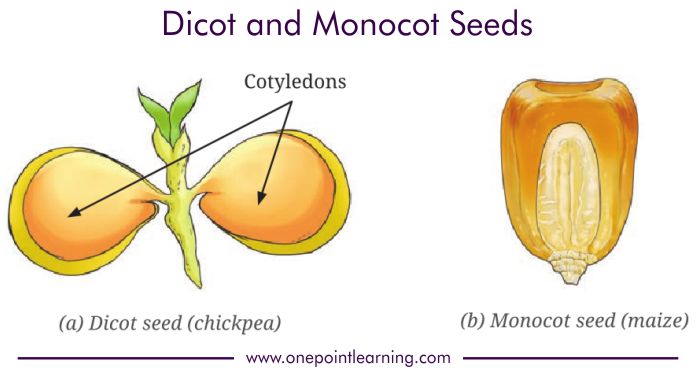
- Dicotyledons (dicots): Plants with two cotyledons (seed leaves) in their seeds. They have reticulate venation (net-like pattern) in their leaves and taproots. Examples include pea, mango, and neem.
- Monocotyledons (monocots): Plants with one cotyledon in their seeds. They have parallel venation in their leaves and fibrous roots. Examples include rice, wheat, and maize.
Grouping of Animals
Based on movement: Animals can be grouped based on how they move. For example, some animals walk, some fly, and some swim.
Biodiversity and Environmental Conditions
- Variation in biodiversity: Different regions have different types of plants and animals due to varying environmental conditions. For example, deserts have different plants and animals compared to rain forests.
- Adaptations: Adaptations are special features that help plants and animals survive in a particular environment. For instance, cacti have spines to reduce water loss in deserts, while polar bears have thick fur to stay warm in cold climates.
Habitats
- Terrestrial habitat: Plants and animals that live on land are called terrestrial. Examples of terrestrial habitats include forests, grasslands, and deserts.
- Aquatic habitat: Plants and animals that live in water are called aquatic. Examples of aquatic habitats include oceans, rivers, lakes, and ponds.
Loss of Biodiversity
Habitat destruction: When humans damage or destroy habitats, plants and animals lose their homes, food, and other resources. This can lead to a loss of biodiversity.
Consequences: Loss of biodiversity can have negative impacts on ecosystems and human well-being. For example, it can affect food production, climate regulation, and the availability of medicines.
Protection of Biodiversity
Importance: It is crucial to protect biodiversity to ensure a healthy planet for future generations.
Actions: We can protect biodiversity through conservation efforts, habitat restoration, and sustainable practices. By protecting biodiversity, we are helping plants and animals to survive and thrive.
Diversity in the living world worksheet overview
Class 6 Science Chapter 2 MCQs
1.Who invited Dr. Radhu and Maniram chacha in school?
a. Teacher b. Parents c. Principle d. Students
2. What type of venation do the leaves of a hibiscus plan have?
a. Parallel b. Reticulate c. Spiral d. None
3. A _____ plant has a taproot and its leaves have reticulate venation.
a. Terrestrial b. Sadabahar c. Aquatic d. None
4. ________ plant has fibrous roots and parallel venation in its leaves.
a. Chana b. Bajra c. Wheat d. Maize
5. All types of animals are use for moving one place to another place.
a. Legs b. Wings c. Fins d. All
Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Fill in the Blanks
1.Dr. Raghu informed them that each bird has a unique _______.
2.Trees provide _____ and _____ to some animals.
3.A _______ pattern of veins on both sides of a thick middle vein.
4._______ them on the basis of common features.
5.The pattern of veins on the leaf is called ______.
Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Question Answer
Que. What is diversity?
Ans. Diversity refers to the variety of all living things and their interactions.
Que. What does Dr. Raghu ask the students to notice in the park?
Ans. Dr. Raghu asks the students to notice the different types of plants, animals, and their interactions in the park.
Que. What are the variation show in the plants?
Ans. The variations shown in plants include their size, shape, color, leaves, roots, and flowers.
Que. Which states are declared as Protected areas the Great Indian Bustards?
Ans. The Great Indian Bustard is protected in Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh.
Que. How do plants adapt to survive in deserts?
Ans. Plants adapt to survive in deserts by having thick, fleshy stems to store water, deep roots to reach underground water sources, and reduced leaf size to minimize water loss.