The chapter 12: Earth Moon and the Sun describes the natural phenomena resulting from the rotation and revolution of the Earth, Moon, and the Sun.
Every day we observe the Sun rising in the east and setting in the west, days changing into nights, seasons repeating every year, and occasional eclipses.
This chapter explains rotation and revolution of the Earth, day–night cycle, seasons, changing night sky, and solar and lunar eclipses, helping students connect daily observations with scientific reasoning.
Earth Moon and the Sun Worksheet
Our worksheets offer a wide range of practice questions, including MCQs, fill-in-the-blanks, and short and long answer questions. Aligned with the latest curriculum, these worksheets promote critical thinking through concept-based activities, simple experiments, and real-life applications.
With engaging and well-structured content, our worksheets help students strengthen their understanding of classroom concepts, prepare effectively for examinations, and build a strong foundation in science.
Through simple observations and activities, this chapter helps us understand:
- Why day and night occur due to the rotation of the Earth
- Why the Sun, Moon, and stars appear to move across the sky
- How the Earth’s revolution around the Sun leads to changing seasons
- Why different constellations are visible in different months of the year
- How and why solar and lunar eclipses occur
- Why days are longer in summer and shorter in winter
- Why seasons are opposite in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres
Overall, this chapter helps students connect everyday observations—such as sunrise, sunset, seasons, and eclipses—with scientific explanations, building a strong foundation in astronomy and Earth science.
Also download:
Social Science worksheets for class 7
Class 7th Science NCERT Solutions Curiosity
Malhar Hindi Worksheet for Class 7
Science Class 7 chapter 12 Study Notes
Rotation of the Earth
- Rotation is the spinning of the Earth on its own axis.
- The Earth rotates from West to East.
- One complete rotation takes about 24 hours.
Rotation causes:
- Day and night
- Apparent movement of the Sun, Moon, and stars across the sky
- Sunrise occurs earlier in the eastern parts of India than the western parts.
Day and Night
- Only half of the Earth receives sunlight at any time.
- The illuminated part experiences day, while the other part experiences night.
- Sunrise happens when a place moves into sunlight; sunset occurs when it moves into darkness.
Apparent Motion of Stars
- Stars appear to move from east to west due to Earth’s rotation.
- The Pole Star (Dhruva Tara) appears almost stationary.
- Constellations like Saptarishi (Big Dipper) seem to rotate around the Pole Star.
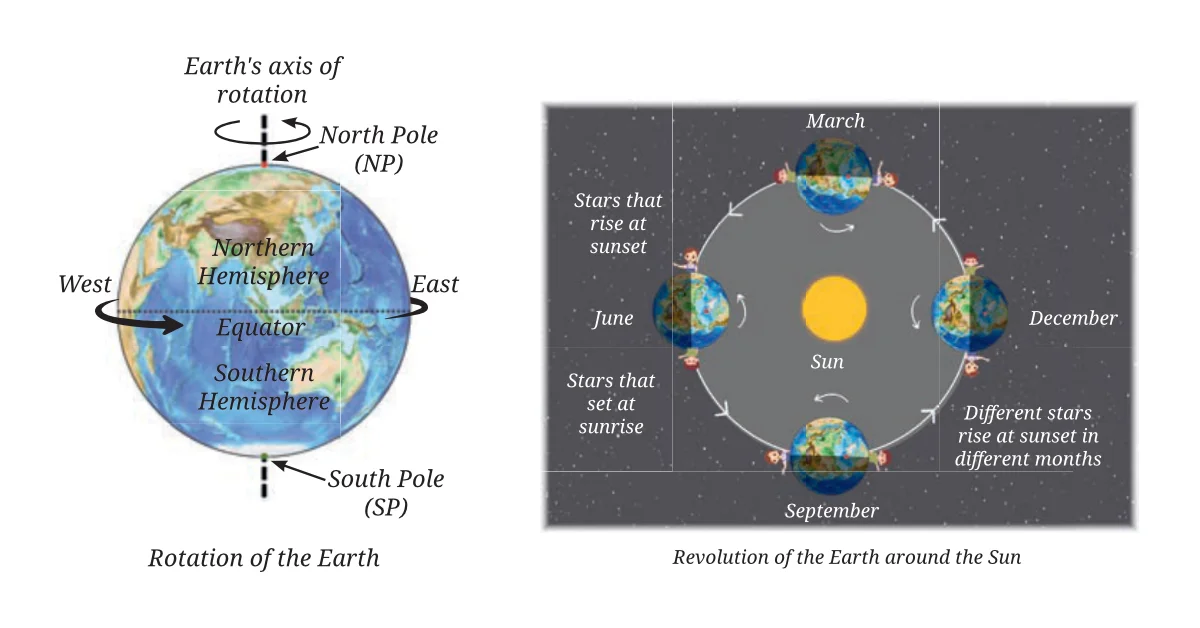
Revolution of the Earth
- Revolution is the movement of the Earth around the Sun.
- The Earth completes one revolution in 365 days and 6 hours.
- The path followed by Earth is called its orbit.
Changing Night Sky
- Because the Earth revolves around the Sun, we see different constellations in different months.
- Stars seen in summer nights are different from those seen in winter nights.
Seasons on the Earth
Seasons occur due to:
- Tilt of Earth’s axis
- Spherical shape of the Earth
- Earth’s axis is tilted and remains tilted while revolving.
- Northern Hemisphere:
- June → Summer (longer days)
- December → Winter (shorter days)
- Southern Hemisphere experiences opposite seasons.
Important days:
- Summer Solstice: ~21 June (longest day)
- Winter Solstice: ~22 December (shortest day)
- Equinoxes: ~21 March & ~23 September (equal day and night)
Eclipses
(a) Solar Eclipse
Occurs when the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth.
Types:
- Total solar eclipse
- Partial solar eclipse
- Never look directly at the Sun during an eclipse.
(b) Lunar Eclipse
- Occurs when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon.
- Happens only on a full moon day.
- Safe to view with naked eyes.
Earth, Moon and the Sun Question Answers
Q1. What is rotation?
Answer: Rotation is the spinning of the Earth on its own imaginary axis that passes through the North Pole and the South Pole. During rotation, every part of the Earth moves in a circular path around this axis.
Q2. What causes day and night on the Earth?
Answer: Day and night are caused by the rotation of the Earth. The side of the Earth facing the Sun experiences day, while the side away from the Sun experiences night. As the Earth rotates, places move alternately into sunlight and darkness.
Q3. What is revolution?
Answer: Revolution is the movement of the Earth around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit. While revolving, the Earth also continues to rotate on its axis.
Q4. Why does the Pole Star appear stationary in the sky?
Answer: The Pole Star appears stationary because the Earth’s axis of rotation points almost directly towards it. As a result, other stars seem to move around the Pole Star, while it remains fixed in position.
Q5. What causes seasons on the Earth?
Answer: Seasons occur due to the tilt of the Earth’s axis and its spherical shape. As the Earth revolves around the Sun with its axis tilted, different parts of the Earth receive different amounts of sunlight during the year.